Without wires and cables, the functioning of production, energy, communications and many other industries is impossible. And not a single house or apartment is complete without wiring. As diverse as the tasks solved with the help of electrical networks and the conditions in which they have to operate, the classification of existing products is just as wide. For the consumer to accurately purchase the desired product and correctly connect to the network, manufacturers must comply with generally accepted standards in the issue of marking wires by colour.
Safety First
For people whose work is constantly connected to electricity, it will not be difficult to recognize the wires both by colour and by alphanumeric markings. She will talk about:
- the material from which the cores and insulation are made;
- purpose of the cable;
- cross-sectional area;
- operating voltage and other features.
And for a person who deals with electricity at the household level, it is enough to understand the color marking of wires. Then it will not be difficult for him to determine the location of the phases and grounding. The risk of electric shock is reduced significantly, and repair or installation work is carried out much faster and without the involvement of specialists.
Specifics Of Various Types Of Cable Products
Before talking about marking, it is worth determining what the difference is between cable, wire and cord.
Various types of cables can be used not only on the surface but also underground, in water. This is possible because one or more insulated cores are protected by a special sheath. It can be made of various materials that can withstand aggressive environmental conditions.
As for electrical wires, they also contain wires or strands that are twisted or insulated from each other. They are covered with a protective non-metallic sheath or winding, which does not imply their lying in the ground.
A cord is a wire containing flexible and insulated conductors. Using this type of cable product, various household devices and devices that are mobile or often move from place to place are connected to the network.
The classification of cable products depending on their purpose is as follows:
- Power products. These include SIP and VVG wires. The latter variety is suitable for installing electrical wiring and lighting indoors, connecting electrical installations. Self-supporting insulated wire (SIP) is used in the construction of overhead power lines and the creation of branches to residential buildings and buildings. The number of conductive cores in products marked VVG varies from 1 to 6. For the SIP variety, this figure ranges from 1 to 4.
- The purpose of RF cables is to transmit a signal from one device to another.
- Control products are needed to power devices and are indispensable in remote control systems. GOST allows the number of conductive cores in them from 4 to 37 pcs.
- To coordinate the operation of instruments and devices at a distance, control wires are used along with the control type. Current-carrying cores in such products can be from 3 to 108 pcs.
- A separate type of communication cable will be required for subscribers to be able to exchange information at a distance. Within this group, there is a division into high- and low-frequency types of products.
Colour As A Source Of Information
Color marking of wires has been used for a long time; it has proven to be convenient and informative. In this regard, no one is going to change it, and knowledge about it will be relevant at any time.
A DC circuit involves the use of only two wires: positive (“+” plus) and negative (“-” minus). Charge conductors with a minus sign are marked in black (or blue). The wires that carry a positive charge are covered in red insulation. The middle conductor in a DC circuit is blue.
Color designation of power and other types of cable products
Color marking for SIP or VVG wires comes down to the following rules:
- The yellow-green color will indicate grounding.
- Zero will give a blue or blue tint to the insulating material.
- The phase conductor will be brown or black. But the rules for electrical installations allow the marking color to change to red, gray and even purple shades.
In single-phase networks, where there is practice of using SIP cables, the neutral working conductor can be combined with the grounding conductor. In this case, the marking will look like a yellow-green wire with blue marks, which are placed at both ends of the line during installation.
Three-phase AC networks assume that the SIP cable cores will have the following colors:
- yellow, green and red for phases A, B and C respectively;
- the blue colour is reserved for highlighting the working zero;
- the green-yellow colour indicates grounding.
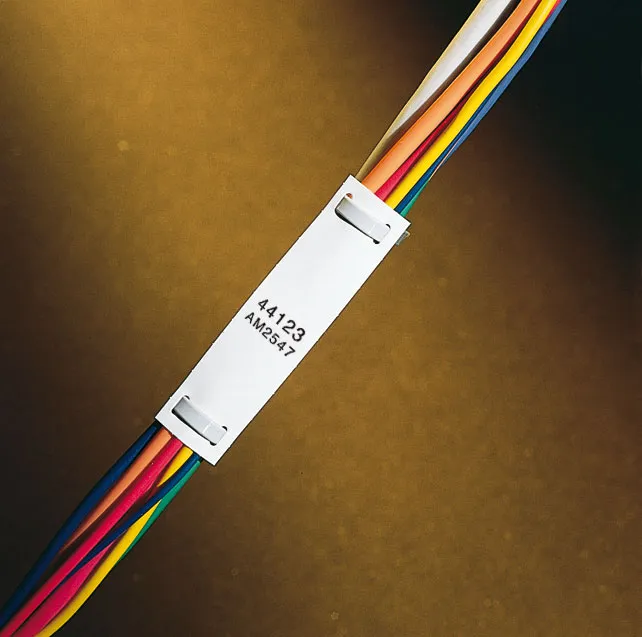

When a SIP cable is used during the installation of power lines, tags with information about the purpose and parameters are additionally attached to it. This marking also allows you to navigate objects where there are many wires of the same type.
Since AC networks are created using colour-coded SIP wires, not only the work at the installation stage is simplified. Color coding makes it easier to maintain and repair networks and helps reduce accidents. And the unpleasant consequences of electric shock can be fatal. Therefore, designating SIP wires and other types by colour is a necessary precaution and a smart solution that makes the work of installers and users of electrical networks easier.
